
GCC companies in Indian Metros and Tier-II Cities
As Global Capability Centers (GCCs) redefine the global operating models for Fortune 500s, multinationals, and fast-growing tech companies, India’s urban ecosystem stands at the very heart of this transformation. While iconic metros like Bengaluru, Hyderabad, and Mumbai are synonymous with the GCC revolution, a new wave of opportunity is surging in India’s dynamic tier-II cities. This evolution isn’t just about geographical spread, but a strategic shift in where and how global business delivers innovation, agility, and value.
Table of Contents
Leading Clusters of GCC companies in Indian Metros and Tier-II cities
GCC companies in Bengaluru
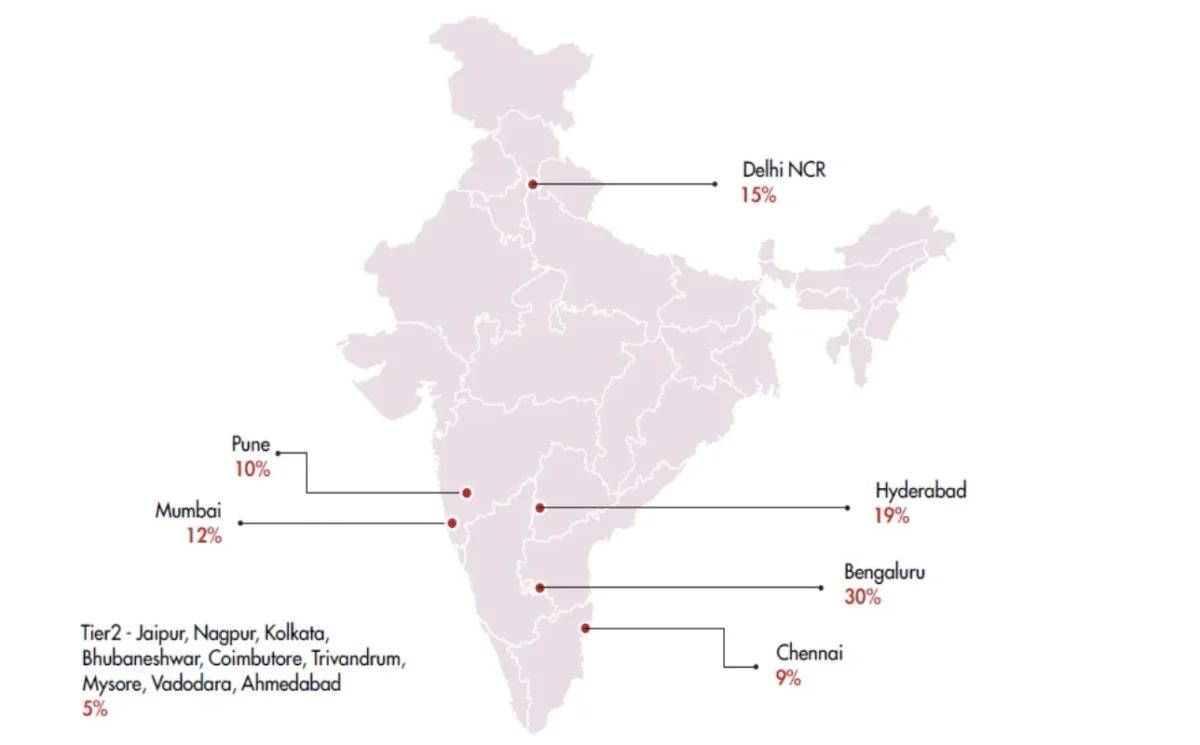
Bengaluru is often called the “Silicon Valley of Asia” and is home to more than 30% of all Indian GCCs. It boasts a talent base exceeding 380,000 just in Fortune 500 GCCs, and over 1,400 high-growth tech startups, making it the first stop for global enterprises seeking software engineering, advanced R&D, and business analytics expertise.
GCC companies in Hyderabad
Hyderabad’s GCC story has exploded in the last decade, with over 19% of all Indian GCCs established here. Its success is powered by proactive state policy, expanding infrastructure (like HITEC City), and lower operational costs. Hyderabad has become a strategic hub for life sciences, pharma, artificial intelligence, and digital engineering, attracting top global names in healthcare and technology.
GCC companies in Mumbai and Delhi NCR
Mumbai, India’s commercial capital, remains the prime hub for banking, financial services, and insurance (BFSI) capability centers. Leading players in fintech, insurance, and analytics set up in Mumbai for proximity to India’s financial ecosystem. Delhi NCR attracts companies in compliance, regulatory, and analytical services, further augmenting India’s leadership in knowledge-driven processes.
GCC companies in Pune and Chennai
Pune and Chennai host a growing concentration of automotive, engineering, and product design GCCs. With strong ties to manufacturing supply chains and access to both engineering and business management talent, these cities are increasingly central to global R&D and supply chain digital transformation.
Quick Stats (2025 Est.) on GCC companies in Indian Metros and Tier-II Cities:
| City | Estimated GCC Centers | Major Sectors | Unique Strengths |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bengaluru | 380+ | Tech, AI, R&D, Retail | Largest talent pool, tech startup hub |
| Hyderabad | 190+ | Pharma, Tech, Health | Policy incentives, cost advantages |
| Mumbai | 80+ | BFSI, Retail, Analytics | Finance cluster, regulatory center |
| Delhi NCR | 90+ | Analytics, RegTech | Proximity to government, fintech |
| Pune | 85+ | Automotive, Engg, Tech | Talent-academia connect, cost |
| Chennai | 90+ | Automotive, Manufacturing | Supply chain, product design |
Related Articles
- Global Capability Centres in India: A Strategic Hub for Innovation
- Investing in Global Capability Centres in India
- H1-B Visa Shock – Leading GCC Companies in India 2025 Beyond
Why Indian Metros Continue to Attract GCC companies
- Unmatched Digital Talent Ecosystem: Annually, over 2.5 million STEM graduates join the workforce. Established metros offer direct access to premier institutes (IITs, IISc, top business schools), and a continuum of talent across tech, business, life sciences, and analytics. This deep bench is crucial as GCCs shift from transactional work to specialist and leadership functions.
- Robust Digital and Physical Infrastructure: Tier-I metros offer world-class office spaces, reliable 5G connectivity, major airport links, and advanced business parks. Areas like Bengaluru’s Outer Ring Road, Hyderabad’s Gachibowli, and Navi Mumbai’s CBD are synonymous with high-spec tech campuses and collaborative innovation zones.
- Ecosystem Synergy: Startups, Academia, Policy: India’s metros are not just talent magnets but vibrant ecosystems. GCCs partner with startups for agile innovation, work with universities on curriculum design, and enjoy robust government support—from Karnataka’s landmark GCC policy to Telangana’s fast-track approvals.
- Innovation-Ready Policies and Incentives: State governments in metros have pioneered special incentives—tax breaks, SEZ benefits, rent subsidies, and skill development grants. Karnataka, Telangana, and Maharashtra, for example, have each rolled out dedicated GCC policies to attract and retain global investment.
The Tier-II City Emergence: Next-Generation GCC Frontiers
With rising real estate and talent costs in metros, companies are looking beyond the obvious. The next wave of GCC growth is heading to tier-II urban centers, such as Jaipur, Ahmedabad, Coimbatore, Indore, Trivandrum, Vizag, and Bhubaneswar. While these cities currently account for under 10% of total GCCs, all research indicates that their share will grow rapidly in the next decade.
- Opportunities in Tier-II Cities: Talent Pool Expansion: New IITs, NITs, and private universities in tier-II cities have begun producing job-ready engineers and data analysts.
- Cost Advantages: Rent, salaries, and operating overheads can be 30-40% less than in top metros, enabling leaner, more agile innovation centers.
- Quality of Life: A less congested environment, improved urban planning, and family-friendly amenities are attractive for talent looking to relocate.
- Government Push: State policies now explicitly target tier-II growth—Uttar Pradesh aims for 1,000+ new GCCs, offering stamp duty waivers, payroll subsidies, and tailored sector incentives.
What Makes a City Attractive for Global Capability Centers?
- Talent and Workforce Readiness
- Access to STEM/analytics graduates, availability of niche skills, and strong local academia-industry partnerships
- Ecosystem Collaboration
- Proximity to startups, tech parks, research labs, and robust legal/consulting service providers
- Physical and Digital Infrastructure
- Grade-A real estate, reliable power, transport connectivity, and digital backbone (5G, cloud hubs)
- Government and Policy Support
- Investment incentives, fiscal benefits, single-window clearances, skill-building programs, regulatory stability
- Quality of Life
- Affordable housing, amenities for expats, urban safety, international schools
A few GCC Companies in Indian Metros and Tier-II cities
| Hyderabad | Bangalore | Pune | Chennai |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft | JPMorgan Chase | Cummins InIT | Caterpillar Inc. |
| Goldman Sachs | TransUnion | ChainSys Corporation | |
| Amazon | Microsoft | SA TechnolPune | Banca Sella |
| Apple | Amazon | Amdocs | Bentley Systems |
| Salesforce | IBM | IBM Global Services | Adidas |
| JP Morgan Chase | Samsung | Wipro | Ericsson |
| HSBC | Cargill | Capgemini | Delphi Automotive PLC |
| Novartis | Guidewire Software | Dassault Systemes | Extreme Networks Inc. |
| Dr. Reddy’s | British telecom | BMC Software | EY |
| Micron Technology | Brocade Communication (Braodcom) | BMW Group | Fiserv |
| AMD | Cambium Networks | Bridgestone | Flex Ltd |
| Qualcomm | Capco (Wipro) | Brose Fahrzeugteile SE & Co. KG | Flowserve |
| Boeing | Cargill | Carraro | Franklin Templeton Investments |
| ZF Lifetec | CGI | Cummins | Frost & Sullivan |
| Bosch | Coca-Cola | Cytiva | Genesys International Corporation Limited |
How Tier-II Cities Can Attract More GCCs: A Blueprint for Growth
While metros have a head start, tier-II cities can accelerate their GCC growth with the right holistic strategy:
- Talent Pipeline Development: Forge deeper industry-academia connect—curriculum co-creation, joint R&D labs, internship programs with local colleges.
- Launch state-sponsored skilling and upskilling initiatives targeting AI, cybersecurity, and digital business skills
- Proactive Local Government Incentives: Offer tailored fiscal incentives—subsidized workspace, tax reliefs, and payroll reimbursements for initial hiring
- Fast-track regulatory clearances and set up single-window investment cells to reduce time and uncertainty
- Infrastructure Readiness: Invest ahead in plug-and-play office parks, reliable power, broadband, and airport connectivity
- Enable mixed-use smart city planning to blend work, life, and innovation spaces
- Cultivate Start-Up and Innovation Culture: Seed local incubators, promote entrepreneurship, and facilitate cross-pollination between startups and GCCs
- Host hackathons, digital summits, and special events to put the city on the business innovation map
- Brand Building: Tell Compelling Stories: Showcase successful GCC stories (even small-scale “Nano GCCs”) to attract global attention
- Position the city as a center for niche expertise (e.g., fintech in Jaipur, AI in Indore, digital health in Trivandrum)
Nano GCCs and Specialized Hubs: The Next GCC Wave
A noteworthy trend from recent years is the rise of Nano GCCs—small, highly specialized centers focused on emerging tech (AI, analytics, cybersecurity) and rapid product innovation. These centers often serve as pilots for larger GCC operations and are particularly viable in tier-II cities, offering global companies’ agility, risk diversification, and access to “fresh” industry talent without the scale requirements of larger campuses.
Future of GCC Companies in Indian Cities
India’s status as the epicenter of the global GCC revolution is set to endure, as both metros and tier-II cities position themselves at the cutting edge of digital transformation, AI, and innovation-driven value creation. If metros remain the backbone, tier-II cities can become the wings that drive GCC growth into new domains and geographies.
